The City of Miami will become a tax-free city with virtual currency!

The city of Miami, Florida, USA, has become a popular destination for tech companies and VCs over the past year.
Goldman Sachs and Softbank have set up offices. In crypto-related activities, Blockchain.com is moving its headquarters from New York to Miami. The exchange FTX is also opening an office.
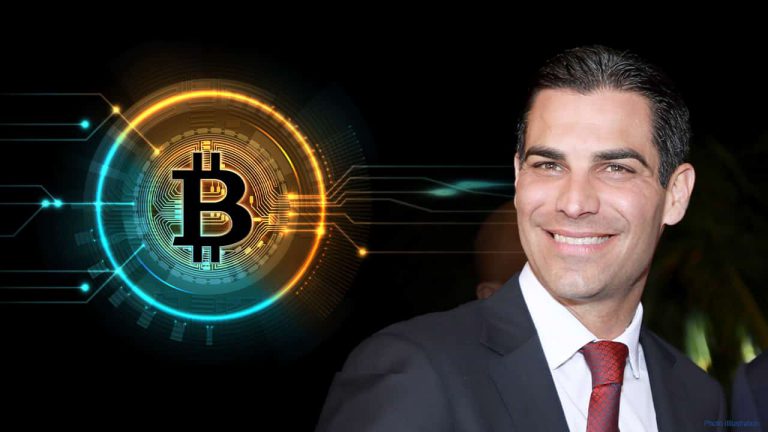
Miami Mayor Francis Suarez has a plan to “make Miami a cryptocurrency innovation hub.
They will make the city tax-free in the future. Virtual currency will be used in place of tax revenue.
Miami is considering becoming a crypto-friendly city and using bitcoin to make payments, pay taxes, and pay fees to the city.

There is a project called CityCoins that uses virtual currency to revitalize communities. The project “allows communities to support cities and offers crypto rewards to individual contributors and cities,” and uses the Stacks chain.
The mechanism is open to all users.
STX Tokens (Stacks Token) can be sent to CityCoin contracts (where they can operate) to mine MIAs (complex computer work to turn them into digital currency) at random.
The finished MIA…
30% will be accumulated in a wallet dedicated to the City of Miami.
70% is allocated to miners (those who did the work): staking (interest) is allocated to users who locked (deposited) MIAs. (STX compensation) *See note below
MIA is a currency voluntarily initiated by the CityCoins community and launched on August 3, 2021.
Then the Stack community and others who wanted to support the City of Miami sent SNX for MIA mining and funds were withheld for the City of Miami On August 26, the exchange Okcoin listed MIA.
And on September 13, the Miami City Council approved to receive the pending amount that had been saved up until then as a donation!
Currency is something that is supplied by continually stimulating demand. This is an experimental story about the possibility of creating a new economic zone by making the regional transit system of Miami a virtual currency.
◆Notes
Staking is a mechanism whereby by holding a particular virtual currency, one contributes to the management of the currency’s blockchain network and is rewarded in return.
Strictly speaking, the virtual currency must not only be held, but also locked (deposited) on the network. The analogy would be similar to a system in which legal tender is saved in a bank account and interest is received after a certain period of time.
Staking can be done with currencies that employ the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. Therefore, currencies that employ PoW (Proof of Work), such as Bitcoin and, as of January 2020, Ethereum, are not eligible.